Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models : Improved DDPM
DDPM을 개선시킨 논문을 발견하게 되어 공부하게 되었습니다. DDPM에 대해 한층 더 잘 알게된 경험이었어서 꼭 한번쯤 읽어보시는걸 추천드립니다 :) Introduction 본 논문에서 제시하는 바는 3가지 입
deepseow.tistory.com
Code Source
https://github.com/lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch
GitHub - lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch: Implementation of Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model in Pytorch
Implementation of Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model in Pytorch - GitHub - lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch: Implementation of Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model in Pytorch
github.com
https://github.com/openai/improved-diffusion
GitHub - openai/improved-diffusion: Release for Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Release for Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models - GitHub - openai/improved-diffusion: Release for Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
github.com
Learning Variance
먼저 U-Net에서 출력 차원을 2배로 함.
default_out_dim = channels * (1 if not learned_variance else 2)
확장된 출력 차원을 v로 하고 아래의 공식을 통해 다음 step의 분산을 얻음.
(Model = U-Net)

def p_mean_variance(self, *, x, t, clip_denoised, model_output = None):
model_output = default(model_output, lambda: self.model(x, t))
pred_noise, var_interp_frac_unnormalized = model_output.chunk(2, dim = 1)
min_log = extract(self.posterior_log_variance_clipped, t, x.shape)
max_log = extract(torch.log(self.betas), t, x.shape)
var_interp_frac = unnormalize_to_zero_to_one(var_interp_frac_unnormalized)
model_log_variance = var_interp_frac * max_log + (1 - var_interp_frac) * min_log
model_variance = model_log_variance.exp()
x_start = self.predict_start_from_noise(x, t, pred_noise)
if clip_denoised:
x_start.clamp_(-1., 1.)
model_mean, _, _ = self.q_posterior(x_start, x, t)
return model_mean, model_variance, model_log_variance
모델이 예측한 평균과 분산, q_posterior의 평균과 분산이 나타내는 확률분포의 KL-divergence를 vb_loss라고 함.
def p_losses(self, x_start, t, noise = None, clip_denoised = False):
noise = default(noise, lambda: torch.randn_like(x_start))
x_t = self.q_sample(x_start = x_start, t = t, noise = noise)
# model output
model_output = self.model(x_t, t)
# calculating kl loss for learned variance (interpolation)
true_mean, _, true_log_variance_clipped = self.q_posterior(x_start = x_start, x_t = x_t, t = t)
model_mean, _, model_log_variance = self.p_mean_variance(x = x_t, t = t, clip_denoised = clip_denoised, model_output = model_output)
# kl loss with detached model predicted mean, for stability reasons as in paper
detached_model_mean = model_mean.detach()
kl = normal_kl(true_mean, true_log_variance_clipped, detached_model_mean, model_log_variance)
kl = meanflat(kl) * NAT
decoder_nll = -discretized_gaussian_log_likelihood(x_start, means = detached_model_mean, log_scales = 0.5 * model_log_variance)
decoder_nll = meanflat(decoder_nll) * NAT
# at the first timestep return the decoder NLL, otherwise return KL(q(x_{t-1}|x_t,x_0) || p(x_{t-1}|x_t))
vb_losses = torch.where(t == 0, decoder_nll, kl)
# simple loss - predicting noise, x0, or x_prev
pred_noise, _ = model_output.chunk(2, dim = 1)
simple_losses = self.loss_fn(pred_noise, noise)
return simple_losses + vb_losses.mean() * self.vb_loss_weight
Cosine Schedule
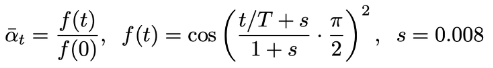
def cosine_beta_schedule(timesteps, s=0.008):
steps = timesteps + 1
x = torch.linspace(0, timesteps, steps)
alphas_cumprod = torch.cos(((x / timesteps) + s) / (1 + s) * torch.pi * 0.5) ** 2
alphas_cumprod = alphas_cumprod / alphas_cumprod[0]
betas = 1 - (alphas_cumprod[1:] / alphas_cumprod[:-1])
return torch.clip(betas, 0.0001, 0.9999)
Reducing Gradient Noise
훈련 중 무작위가 아닌 샘플러에서 t와 가중치를 받는다.
def forward_backward(self, batch, cond):
zero_grad(self.model_params)
for i in range(0, batch.shape[0], self.microbatch):
micro = batch[i : i + self.microbatch].to(dist_util.dev())
micro_cond = {
k: v[i : i + self.microbatch].to(dist_util.dev())
for k, v in cond.items()
}
last_batch = (i + self.microbatch) >= batch.shape[0]
t, weights = self.schedule_sampler.sample(micro.shape[0], dist_util.dev())
compute_losses = functools.partial(
self.diffusion.training_losses,
self.ddp_model,
micro,
t,
model_kwargs=micro_cond,
)
losses = compute_losses()
loss = (losses["loss"] * weights).mean()
log_loss_dict(
self.diffusion, t, {k: v * weights for k, v in losses.items()}
)
loss.backward()샘플러 종류는 해당 코드 참고.
Improving Sampling Speed
Sampling stride 지정 함수
def space_timesteps(num_timesteps, section_counts):
"""
Create a list of timesteps to use from an original diffusion process,
given the number of timesteps we want to take from equally-sized portions
of the original process.
For example, if there's 300 timesteps and the section counts are [10,15,20]
then the first 100 timesteps are strided to be 10 timesteps, the second 100
are strided to be 15 timesteps, and the final 100 are strided to be 20.
If the stride is a string starting with "ddim", then the fixed striding
from the DDIM paper is used, and only one section is allowed.
:param num_timesteps: the number of diffusion steps in the original
process to divide up.
:param section_counts: either a list of numbers, or a string containing
comma-separated numbers, indicating the step count
per section. As a special case, use "ddimN" where N
is a number of steps to use the striding from the
DDIM paper.
:return: a set of diffusion steps from the original process to use.
"""
if isinstance(section_counts, str):
if section_counts.startswith("ddim"):
desired_count = int(section_counts[len("ddim") :])
for i in range(1, num_timesteps):
if len(range(0, num_timesteps, i)) == desired_count:
return set(range(0, num_timesteps, i))
raise ValueError(
f"cannot create exactly {num_timesteps} steps with an integer stride"
)
section_counts = [int(x) for x in section_counts.split(",")]
size_per = num_timesteps // len(section_counts)
extra = num_timesteps % len(section_counts)
start_idx = 0
all_steps = []
for i, section_count in enumerate(section_counts):
size = size_per + (1 if i < extra else 0)
if size < section_count:
raise ValueError(
f"cannot divide section of {size} steps into {section_count}"
)
if section_count <= 1:
frac_stride = 1
else:
frac_stride = (size - 1) / (section_count - 1)
cur_idx = 0.0
taken_steps = []
for _ in range(section_count):
taken_steps.append(start_idx + round(cur_idx))
cur_idx += frac_stride
all_steps += taken_steps
start_idx += size
return set(all_steps)
U-Net에 입력될 시간 단계 t를 변경된 sampling stride에 따라 리스케일링 하는 클래스
class _WrappedModel:
def __init__(self, model, timestep_map, rescale_timesteps, original_num_steps):
self.model = model
self.timestep_map = timestep_map
self.rescale_timesteps = rescale_timesteps
self.original_num_steps = original_num_steps
def __call__(self, x, ts, **kwargs):
map_tensor = th.tensor(self.timestep_map, device=ts.device, dtype=ts.dtype)
new_ts = map_tensor[ts]
if self.rescale_timesteps:
new_ts = new_ts.float() * (1000.0 / self.original_num_steps)
return self.model(x, new_ts, **kwargs)
훈련된 가중치로 해당 클래스 인스턴스를 만들고 새로운 확산 단계에 따라 샘플링하면 됨.
class SpacedDiffusion(GaussianDiffusion):
"""
A diffusion process which can skip steps in a base diffusion process.
:param use_timesteps: a collection (sequence or set) of timesteps from the
original diffusion process to retain.
:param kwargs: the kwargs to create the base diffusion process.
"""
def __init__(self, use_timesteps, **kwargs):
self.use_timesteps = set(use_timesteps)
self.timestep_map = []
self.original_num_steps = len(kwargs["betas"])
base_diffusion = GaussianDiffusion(**kwargs) # pylint: disable=missing-kwoa
last_alpha_cumprod = 1.0
new_betas = []
for i, alpha_cumprod in enumerate(base_diffusion.alphas_cumprod):
if i in self.use_timesteps:
new_betas.append(1 - alpha_cumprod / last_alpha_cumprod)
last_alpha_cumprod = alpha_cumprod
self.timestep_map.append(i)
kwargs["betas"] = np.array(new_betas)
super().__init__(**kwargs)
def p_mean_variance(
self, model, *args, **kwargs
): # pylint: disable=signature-differs
return super().p_mean_variance(self._wrap_model(model), *args, **kwargs)
def training_losses(
self, model, *args, **kwargs
): # pylint: disable=signature-differs
return super().training_losses(self._wrap_model(model), *args, **kwargs)
def _wrap_model(self, model):
if isinstance(model, _WrappedModel):
return model
return _WrappedModel(
model, self.timestep_map, self.rescale_timesteps, self.original_num_steps
)
def _scale_timesteps(self, t):
# Scaling is done by the wrapped model.
return t'코드 리뷰 > Diffusion' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DiffStyler 코드 리뷰 (0) | 2023.01.16 |
|---|---|
| Paint by Example 코드 리뷰 (1) | 2023.01.15 |
| DAAM 코드 리뷰 (1) | 2023.01.12 |
| Latent Diffusion (0) | 2022.12.28 |
| Classifier-Guidance Diffusion (1) | 2022.12.07 |
| Denoising Diffusion Pytorch (1) | 2022.09.25 |


