https://github.com/lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch
GitHub - lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch: Implementation of Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model in Pytorch
Implementation of Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model in Pytorch - GitHub - lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch: Implementation of Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model in Pytorch
github.com
https://huggingface.co/blog/annotated-diffusion
The Annotated Diffusion Model
The Annotated Diffusion Model In this blog post, we'll take a deeper look into Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (also known as DDPMs, diffusion models, score-based generative models or simply autoencoders) as researchers have been able to achieve r
huggingface.co
위의 코드와 포스팅을 기반으로 함.
지금 글은 정리하는 용도로 쓰는 것이기 때문에 공부를 위해서라면 위 포스팅을 읽는 게 더 좋음.
네트워크 도우미
def exists(x):
return x is not None
def default(val, d):
if exists(val):
return val
return d() if isfunction(d) else d
class Residual(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, fn):
super().__init__()
self.fn = fn
def forward(self, x, *args, **kwargs):
return self.fn(x, *args, **kwargs) + x
def Upsample(dim):
return nn.ConvTranspose2d(dim, dim, 4, 2, 1)
def Downsample(dim):
return nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 4, 2, 1)
위치 임베딩
class SinusoidalPositionEmbeddings(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
def forward(self, time):
device = time.device
half_dim = self.dim // 2
embeddings = math.log(10000) / (half_dim - 1)
embeddings = torch.exp(torch.arange(half_dim, device=device) * -embeddings)
embeddings = time[:, None] * embeddings[None, :]
embeddings = torch.cat((embeddings.sin(), embeddings.cos()), dim=-1)
return embeddings트랜스포머의 위치 임베딩을
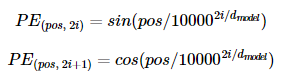
확산 시간 임베딩으로 사용
그룹 정규화
class PreNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, fn):
super().__init__()
self.fn = fn
self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(1, dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.norm(x)
return self.fn(x)
ResNet, ConvNeXT 블록
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, dim_out, groups = 8):
super().__init__()
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim_out, 3, padding = 1)
self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(groups, dim_out)
self.act = nn.SiLU()
def forward(self, x, scale_shift = None):
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.norm(x)
if exists(scale_shift):
scale, shift = scale_shift
x = x * (scale + 1) + shift
x = self.act(x)
return x
class ResnetBlock(nn.Module):
"""https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385"""
def __init__(self, dim, dim_out, *, time_emb_dim=None, groups=8):
super().__init__()
self.mlp = (
nn.Sequential(nn.SiLU(), nn.Linear(time_emb_dim, dim_out))
if exists(time_emb_dim)
else None
)
self.block1 = Block(dim, dim_out, groups=groups)
self.block2 = Block(dim_out, dim_out, groups=groups)
self.res_conv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim_out, 1) if dim != dim_out else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x, time_emb=None):
h = self.block1(x)
if exists(self.mlp) and exists(time_emb):
time_emb = self.mlp(time_emb)
h = rearrange(time_emb, "b c -> b c 1 1") + h
h = self.block2(h)
return h + self.res_conv(x)
class ConvNextBlock(nn.Module):
"""https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545"""
def __init__(self, dim, dim_out, *, time_emb_dim=None, mult=2, norm=True):
super().__init__()
self.mlp = (
nn.Sequential(nn.GELU(), nn.Linear(time_emb_dim, dim))
if exists(time_emb_dim)
else None
)
self.ds_conv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 7, padding=3, groups=dim)
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.GroupNorm(1, dim) if norm else nn.Identity(),
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim_out * mult, 3, padding=1),
nn.GELU(),
nn.GroupNorm(1, dim_out * mult),
nn.Conv2d(dim_out * mult, dim_out, 3, padding=1),
)
self.res_conv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim_out, 1) if dim != dim_out else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x, time_emb=None):
h = self.ds_conv(x)
if exists(self.mlp) and exists(time_emb):
condition = self.mlp(time_emb)
h = h + rearrange(condition, "b c -> b c 1 1")
h = self.net(h)
return h + self.res_conv(x)
Attention
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, heads=4, dim_head=32):
super().__init__()
self.scale = dim_head**-0.5
self.heads = heads
hidden_dim = dim_head * heads
self.to_qkv = nn.Conv2d(dim, hidden_dim * 3, 1, bias=False)
self.to_out = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, dim, 1)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim=1)
q, k, v = map(
lambda t: rearrange(t, "b (h c) x y -> b h c (x y)", h=self.heads), qkv
)
q = q * self.scale
sim = einsum("b h d i, b h d j -> b h i j", q, k)
sim = sim - sim.amax(dim=-1, keepdim=True).detach()
attn = sim.softmax(dim=-1)
out = einsum("b h i j, b h d j -> b h i d", attn, v)
out = rearrange(out, "b h (x y) d -> b (h d) x y", x=h, y=w)
return self.to_out(out)
self.to_qkv = nn.Conv2d(dim, hidden_dim * 3, 1, bias=False)
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim=1)Conv에서 차원을 3배로 늘리고 q,k,v로 분해
lambda t: rearrange(t, "b (h c) x y -> b h c (x y)", h=self.heads), qkv
채널을 attention head의 수만큼 분해하고 x, y를 합침
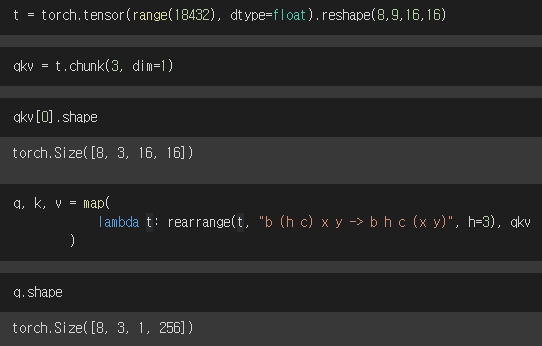
sim = einsum("b h d i, b h d j -> b h i j", q, k)
out = einsum("b h i j, b h d j -> b h i d", attn, v)자동으로 크기 맞춰서 전치하고 내적됨.
선형 복잡성 attention
class LinearAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, heads=4, dim_head=32):
super().__init__()
self.scale = dim_head**-0.5
self.heads = heads
hidden_dim = dim_head * heads
self.to_qkv = nn.Conv2d(dim, hidden_dim * 3, 1, bias=False)
self.to_out = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, dim, 1),
nn.GroupNorm(1, dim))
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim=1)
q, k, v = map(
lambda t: rearrange(t, "b (h c) x y -> b h c (x y)", h=self.heads), qkv
)
q = q.softmax(dim=-2)
k = k.softmax(dim=-1)
q = q * self.scale
context = torch.einsum("b h d n, b h e n -> b h d e", k, v)
out = torch.einsum("b h d e, b h d n -> b h e n", context, q)
out = rearrange(out, "b h c (x y) -> b (h c) x y", h=self.heads, x=h, y=w)
return self.to_out(out)
U-Net
각 다운샘플링/업샘플링 단계는
ResNet/ConvNext 블록 2개 + (groupnorm + Attention + 잔차 연결) + 다운샘플링/업샘플링으로 구성됨.
self.downs.append(
nn.ModuleList(
[
block_klass(dim_in, dim_out, time_emb_dim=time_dim),
block_klass(dim_out, dim_out, time_emb_dim=time_dim),
Residual(PreNorm(dim_out, LinearAttention(dim_out))),
Downsample(dim_out) if not is_last else nn.Identity(),
]
)
)
전체 아키텍처
class Unet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
dim,
init_dim=None,
out_dim=None,
dim_mults=(1, 2, 4, 8),
channels=3,
with_time_emb=True,
resnet_block_groups=8,
use_convnext=True,
convnext_mult=2,
):
super().__init__()
# determine dimensions
self.channels = channels
init_dim = default(init_dim, dim // 3 * 2)
self.init_conv = nn.Conv2d(channels, init_dim, 7, padding=3)
dims = [init_dim, *map(lambda m: dim * m, dim_mults)]
in_out = list(zip(dims[:-1], dims[1:]))
if use_convnext:
block_klass = partial(ConvNextBlock, mult=convnext_mult)
else:
block_klass = partial(ResnetBlock, groups=resnet_block_groups)
# time embeddings
if with_time_emb:
time_dim = dim * 4
self.time_mlp = nn.Sequential(
SinusoidalPositionEmbeddings(dim),
nn.Linear(dim, time_dim),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(time_dim, time_dim),
)
else:
time_dim = None
self.time_mlp = None
# layers
self.downs = nn.ModuleList([])
self.ups = nn.ModuleList([])
num_resolutions = len(in_out)
for ind, (dim_in, dim_out) in enumerate(in_out):
is_last = ind >= (num_resolutions - 1)
self.downs.append(
nn.ModuleList(
[
block_klass(dim_in, dim_out, time_emb_dim=time_dim),
block_klass(dim_out, dim_out, time_emb_dim=time_dim),
Residual(PreNorm(dim_out, LinearAttention(dim_out))),
Downsample(dim_out) if not is_last else nn.Identity(),
]
)
)
mid_dim = dims[-1]
self.mid_block1 = block_klass(mid_dim, mid_dim, time_emb_dim=time_dim)
self.mid_attn = Residual(PreNorm(mid_dim, Attention(mid_dim)))
self.mid_block2 = block_klass(mid_dim, mid_dim, time_emb_dim=time_dim)
for ind, (dim_in, dim_out) in enumerate(reversed(in_out[1:])):
is_last = ind >= (num_resolutions - 1)
self.ups.append(
nn.ModuleList(
[
block_klass(dim_out * 2, dim_in, time_emb_dim=time_dim),
block_klass(dim_in, dim_in, time_emb_dim=time_dim),
Residual(PreNorm(dim_in, LinearAttention(dim_in))),
Upsample(dim_in) if not is_last else nn.Identity(),
]
)
)
out_dim = default(out_dim, channels)
self.final_conv = nn.Sequential(
block_klass(dim, dim), nn.Conv2d(dim, out_dim, 1)
)
def forward(self, x, time):
x = self.init_conv(x)
t = self.time_mlp(time) if exists(self.time_mlp) else None
h = []
# downsample
for block1, block2, attn, downsample in self.downs:
x = block1(x, t)
x = block2(x, t)
x = attn(x)
h.append(x)
x = downsample(x)
# bottleneck
x = self.mid_block1(x, t)
x = self.mid_attn(x)
x = self.mid_block2(x, t)
# upsample
for block1, block2, attn, upsample in self.ups:
x = torch.cat((x, h.pop()), dim=1)
x = block1(x, t)
x = block2(x, t)
x = attn(x)
x = upsample(x)
return self.final_conv(x)
확산 스케줄링
def linear_beta_schedule(timesteps):
beta_start = 0.0001
beta_end = 0.02
return torch.linspace(beta_start, beta_end, timesteps)
def quadratic_beta_schedule(timesteps):
beta_start = 0.0001
beta_end = 0.02
return torch.linspace(beta_start**0.5, beta_end**0.5, timesteps) ** 2
def sigmoid_beta_schedule(timesteps):
beta_start = 0.0001
beta_end = 0.02
betas = torch.linspace(-6, 6, timesteps)
return torch.sigmoid(betas) * (beta_end - beta_start) + beta_start
코사인 스케줄
def cosine_beta_schedule(timesteps, s=0.008):
"""
cosine schedule as proposed in https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.09672
"""
steps = timesteps + 1
x = torch.linspace(0, timesteps, steps)
alphas_cumprod = torch.cos(((x / timesteps) + s) / (1 + s) * torch.pi * 0.5) ** 2
alphas_cumprod = alphas_cumprod / alphas_cumprod[0]
betas = 1 - (alphas_cumprod[1:] / alphas_cumprod[:-1])
return torch.clip(betas, 0.0001, 0.9999)
순방향 확산 과정
각 변수 정의
timesteps = 200
# define beta schedule
betas = linear_beta_schedule(timesteps=timesteps)
# define alphas
alphas = 1. - betas
alphas_cumprod = torch.cumprod(alphas, axis=0)
alphas_cumprod_prev = F.pad(alphas_cumprod[:-1], (1, 0), value=1.0)
sqrt_recip_alphas = torch.sqrt(1.0 / alphas)
# calculations for diffusion q(x_t | x_{t-1}) and others
sqrt_alphas_cumprod = torch.sqrt(alphas_cumprod)
sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod = torch.sqrt(1. - alphas_cumprod)
# calculations for posterior q(x_{t-1} | x_t, x_0)
posterior_variance = betas * (1. - alphas_cumprod_prev) / (1. - alphas_cumprod)
리스트에서 t 인덱스를 가져오고 사이즈 맞춰주는 함수
def extract(a, t, x_shape):
batch_size = t.shape[0]
out = a.gather(-1, t.cpu())
return out.reshape(batch_size, *((1,) * (len(x_shape) - 1))).to(t.device)
이미지 로드
from PIL import Image
import requests
url = 'http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg'
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
image
이미지 전처리
from torchvision.transforms import Compose, ToTensor, Lambda, ToPILImage, CenterCrop, Resize
image_size = 128
transform = Compose([
Resize(image_size),
CenterCrop(image_size),
ToTensor(), # turn into Numpy array of shape HWC, divide by 255
Lambda(lambda t: (t * 2) - 1),
])
x_start = transform(image).unsqueeze(0)
x_start.shapeOutput:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
torch.Size([1, 3, 128, 128])
텐서 → 이미지 역변환 정의
import numpy as np
reverse_transform = Compose([
Lambda(lambda t: (t + 1) / 2),
Lambda(lambda t: t.permute(1, 2, 0)), # CHW to HWC
Lambda(lambda t: t * 255.),
Lambda(lambda t: t.numpy().astype(np.uint8)),
ToPILImage(),
])
순방향 과정 정의
# forward diffusion (using the nice property)
def q_sample(x_start, t, noise=None):
if noise is None:
noise = torch.randn_like(x_start)
sqrt_alphas_cumprod_t = extract(sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape)
sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod_t = extract(
sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape
)
return sqrt_alphas_cumprod_t * x_start + sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod_t * noise확산 시간 t를 인덱스로 알파 누적곱 리스트에서 값을 가져오고 해당 비율만큼 이미지와 노이즈를 섞음
손실 함수 정의
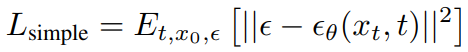
랜덤 노이즈와 시간 단계 t로 노이즈가 추가된 이미지를 얻고 해당 이미지를 보고 모델이 노이즈를 예측한다.
def p_losses(denoise_model, x_start, t, noise=None, loss_type="l1"):
if noise is None:
noise = torch.randn_like(x_start)
x_noisy = q_sample(x_start=x_start, t=t, noise=noise)
predicted_noise = denoise_model(x_noisy, t)
if loss_type == 'l1':
loss = F.l1_loss(noise, predicted_noise)
elif loss_type == 'l2':
loss = F.mse_loss(noise, predicted_noise)
elif loss_type == "huber":
loss = F.smooth_l1_loss(noise, predicted_noise)
else:
raise NotImplementedError()
return loss
샘플링
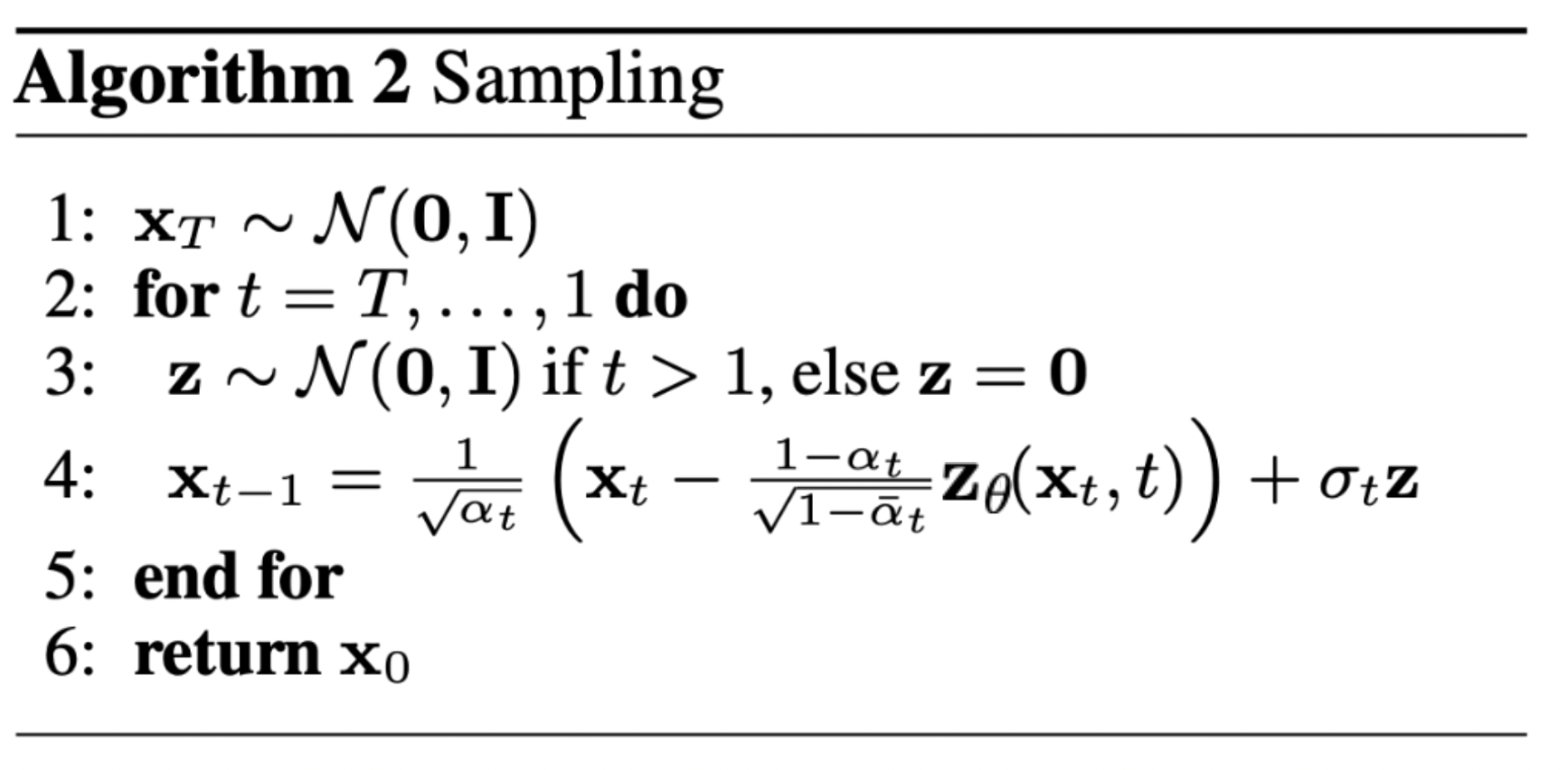
그냥 알고리즘을 코드 구현한 거임.
DDPM에서는 노이즈 제거 후 소량의 노이즈를 다시 추가함.
@torch.no_grad()
def p_sample(model, x, t, t_index):
betas_t = extract(betas, t, x.shape)
sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod_t = extract(
sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x.shape
)
sqrt_recip_alphas_t = extract(sqrt_recip_alphas, t, x.shape)
# Equation 11 in the paper
# Use our model (noise predictor) to predict the mean
model_mean = sqrt_recip_alphas_t * (
x - betas_t * model(x, t) / sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod_t
)
if t_index == 0:
return model_mean
else:
posterior_variance_t = extract(posterior_variance, t, x.shape)
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
# Algorithm 2 line 4:
return model_mean + torch.sqrt(posterior_variance_t) * noise
전체 과정으로 확장
@torch.no_grad()
def p_sample_loop(model, shape):
device = next(model.parameters()).device
b = shape[0]
# start from pure noise (for each example in the batch)
img = torch.randn(shape, device=device)
imgs = []
for i in tqdm(reversed(range(0, timesteps)), desc='sampling loop time step', total=timesteps):
img = p_sample(model, img, torch.full((b,), i, device=device, dtype=torch.long), i)
imgs.append(img.cpu().numpy())
return imgs
@torch.no_grad()
def sample(model, image_size, batch_size=16, channels=3):
return p_sample_loop(model, shape=(batch_size, channels, image_size, image_size))
모델 훈련
모델과 optimizer 정의
from torch.optim import Adam
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model = Unet(
dim=image_size,
channels=channels,
dim_mults=(1, 2, 4,)
)
model.to(device)
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
훈련 개시
무작위 t 시점에서 해당 이미지에 추가된 노이즈를 예측하도록 훈련됨.
from torchvision.utils import save_image
epochs = 5
for epoch in range(epochs):
for step, batch in enumerate(dataloader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
batch_size = batch["pixel_values"].shape[0]
batch = batch["pixel_values"].to(device)
# Algorithm 1 line 3: sample t uniformally for every example in the batch
t = torch.randint(0, timesteps, (batch_size,), device=device).long()
loss = p_losses(model, batch, t, loss_type="huber")
if step % 100 == 0:
print("Loss:", loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# save generated images
if step != 0 and step % save_and_sample_every == 0:
milestone = step // save_and_sample_every
batches = num_to_groups(4, batch_size)
all_images_list = list(map(lambda n: sample(model, batch_size=n, channels=channels), batches))
all_images = torch.cat(all_images_list, dim=0)
all_images = (all_images + 1) * 0.5
save_image(all_images, str(results_folder / f'sample-{milestone}.png'), nrow = 6)
시각화
다양한 시간 단계에서 이미지 시각화
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# use seed for reproducability
torch.manual_seed(0)
# source: https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/auto_examples/plot_transforms.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-plot-transforms-py
def plot(imgs, with_orig=False, row_title=None, **imshow_kwargs):
if not isinstance(imgs[0], list):
# Make a 2d grid even if there's just 1 row
imgs = [imgs]
num_rows = len(imgs)
num_cols = len(imgs[0]) + with_orig
fig, axs = plt.subplots(figsize=(200,200), nrows=num_rows, ncols=num_cols, squeeze=False)
for row_idx, row in enumerate(imgs):
row = [image] + row if with_orig else row
for col_idx, img in enumerate(row):
ax = axs[row_idx, col_idx]
ax.imshow(np.asarray(img), **imshow_kwargs)
ax.set(xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[], xticks=[], yticks=[])
if with_orig:
axs[0, 0].set(title='Original image')
axs[0, 0].title.set_size(8)
if row_title is not None:
for row_idx in range(num_rows):
axs[row_idx, 0].set(ylabel=row_title[row_idx])
plt.tight_layout()plot([get_noisy_image(x_start, torch.tensor([t])) for t in [0, 50, 100, 150, 199]])
노이즈 제거 과정을 gif로 만들기
import matplotlib.animation as animation
random_index = 53
fig = plt.figure()
ims = []
for i in range(timesteps):
im = plt.imshow(samples[i][random_index].reshape(image_size, image_size, channels), cmap="gray", animated=True)
ims.append([im])
animate = animation.ArtistAnimation(fig, ims, interval=50, blit=True, repeat_delay=1000)
animate.save('diffusion.gif')
plt.show()
'코드 리뷰 > Diffusion' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DiffStyler 코드 리뷰 (0) | 2023.01.16 |
|---|---|
| Paint by Example 코드 리뷰 (1) | 2023.01.15 |
| DAAM 코드 리뷰 (1) | 2023.01.12 |
| Latent Diffusion (0) | 2022.12.28 |
| Classifier-Guidance Diffusion (1) | 2022.12.07 |
| Improved DDPM (0) | 2022.09.28 |


